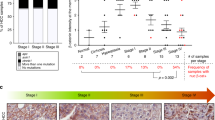
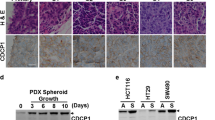
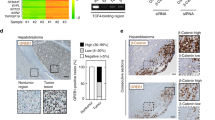
Abstract
Overexpressed or activated hepatocyte growth factor receptor, encoded by the MET proto-oncogene, was found in the majority of colorectal carcinomas (CRCs), whose stepwise progression to malignancy requires transcriptional activation of β-catenin. We here demonstrate that a functional crosstalk between Met and β-catenin signaling sustains and increases CRC cell invasive properties. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulation prompts β-catenin tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation from Met, and upregulates β-catenin expression via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in conditions that mimic those found by the invading and metastasizing cells. Additionally, a transcriptionally active form of β-catenin, known to be oncogenic, enhances Met expression. Furthermore, HGF treatment increases the activity of the β-catenin-regulated T-cell factor transcription factor in cells expressing the wild-type or the oncogenic β-catenin. In the mirror experiments, either Met or β-catenin knocking down also reduces their protein level. In biological assays, β-catenin knocking down abrogates the HGF-induced motile phenotype, whereas active β-catenin fosters ligand-independent cell scattering. Met and β-catenin also cooperate in promoting entry into the cell cycle and in protecting cells from apoptosis. In conclusion, Met and β-catenin pathways are mutually activated in CRC cells. This might generate a self-amplifying positive feedback loop resulting in the upregulation of the invasive growth properties of CRC cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakaki N, Kazi JA, Kazihara T, Ohnishi T, Daikuhara Y . (1998). Involvement of oxidative stress in tumor cytotoxic activity of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245: 211–215.
Berns K, Hijmans EM, Mullenders J, Brummelkamp TR, Velds A, Heimerikx M et al. (2004). A large-scale RNAi screen in human cells identifies new components of the p53 pathway. Nature 428: 431–437.
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, Vande Woude GF . (2003). Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 915–925.
Boon EM, Kovarikova M, Derksen PW, van der Neut R . (2005). MET signalling in primary colon epithelial cells leads to increased transformation irrespective of aberrant Wnt signalling. Br J Cancer 92: 1078–1083.
Boon EM, van der Neut R, van de Wetering M, Clevers H, Pals ST . (2002). Wnt signaling regulates expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase met in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 62: 5126–5128.
Bowers DC, Fan S, Walter KA, Abounader R, Williams JA, Rosen EM et al. (2000). Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor protects against cytotoxic death in human glioblastoma via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase- and AKT-dependent pathways. Cancer Res 60: 4277–4283.
Corso S, Comoglio PM, Giordano S . (2005). Cancer therapy: can the challenge be MET? Trends Mol Med 11: 284–292.
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Miagkov A, Skeel A, Nakaigawa N, Zbar B, Leonard EJ . (2001). Oncogenic mutants of RON and MET receptor tyrosine kinases cause activation of the beta-catenin pathway. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5857–5868.
Derksen PW, de Gorter DJ, Meijer HP, Bende RJ, van Dijk M, Lokhorst HM et al. (2003). The hepatocyte growth factor/Met pathway controls proliferation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 17: 764–774.
Di Renzo MF, Olivero M, Giacomini A, Porte H, Chastre E, Mirossay L et al. (1995). Overexpression and amplification of the met/HGF receptor gene during the progression of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1: 147–154.
Dihlmann S, Kloor M, Fallsehr C, von Knebel Doeberitz M . (2005). Regulation of AKT1 expression by beta-catenin/Tcf/Lef signaling in colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 26: 1503–1512.
Edlund S, Lee SY, Grimsby S, Zhang S, Aspenstrom P, Heldin CH et al. (2005). Interaction between Smad7 and beta-catenin: importance for transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 25: 1475–1488.
Fan S, Gao M, Meng Q, Laterra JJ, Symons MH, Coniglio S et al. (2005). Role of NF-kappaB signaling in hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-mediated cell protection. Oncogene 24: 1749–1766.
Fan S, Ma YX, Wang JA, Yuan RQ, Meng Q, Cao Y et al. (2000). The cytokine hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor inhibits apoptosis and enhances DNA repair by a common mechanism involving signaling through phosphatidyl inositol 3′ kinase. Oncogene 19: 2212–2223.
Fazekas K, Csuka O, Koves I, Raso E, Timar J . (2000). Experimental and clinicopathologic studies on the function of the HGF receptor in human colon cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metast 18: 639–649.
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA, Sugimoto C . (2003). PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene 22: 8983–8998.
Gao M, Fan S, Goldberg ID, Laterra J, Kitsis RN, Rosen EM . (2001). Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor blocks the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis signaling in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 276: 47257–47265.
Giles RH, van Es JH, Clevers H . (2003). Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1653: 1–24.
Gramaglia D, Gentile A, Battaglia M, Ranzato L, Petronilli V, Fassetta M et al. (2004). Apoptosis to necrosis switching downstream of apoptosome formation requires inhibition of both glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation in a BCL-X(L)- and PKB/AKT-independent fashion. Cell Death Differ 11: 342–353.
Gregorieff A, Clevers H . (2005). Wnt signaling in the intestinal epithelium: from endoderm to cancer. Genes Dev 19: 877–890.
Grossmann J . (2002). Molecular mechanisms of ‘detachment-induced apoptosis – Anoikis’. Apoptosis 7: 247–260.
Harris TJ, Peifer M . (2005). Decisions, decisions: beta-catenin chooses between adhesion and transcription. Trends Cell Biol 15: 234–237.
Henderson BR, Fagotto F . (2002). The ins and outs of APC and beta-catenin nuclear transport. EMBO Rep 3: 834–839.
Herynk MH, Tsan R, Radinsky R, Gallick GE . (2003). Down-regulation of c-Met inhibits growth in the liver of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Clin Exp Metast 20: 291–300.
Ireland H, Kemp R, Houghton C, Howard L, Clarke AR, Sansom OJ et al. (2004). Inducible Cre-mediated control of gene expression in the murine gastrointestinal tract: effect of loss of beta-catenin. Gastroenterology 126: 1236–1246.
Khoury H, Naujokas MA, Zuo D, Sangwan V, Frigault MM, Petkiewicz S et al. (2005). HGF converts ErbB2/Neu epithelial morphogenesis to cell invasion. Mol Biol Cell 16: 550–561.
Kim K, Pang KM, Evans M, Hay ED . (2000). Overexpression of beta-catenin induces apoptosis independent of its transactivation function with LEF-1 or the involvement of major G1 cell cycle regulators. Mol Biol Cell 11: 3509–3523.
Kim TH, Xiong H, Zhang Z, Ren B . (2005). beta-Catenin activates the growth factor endothelin-1 in colon cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 597–604.
Lal B, Xia S, Abounader R, Laterra J . (2005). Targeting the c-Met pathway potentiates glioblastoma responses to gamma-radiation. Clin Cancer Res 11: 4479–4486.
Logan CY, Nusse R . (2004). The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20: 781–810.
Lustig B, Behrens J . (2003). The Wnt signaling pathway and its role in tumor development. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129: 199–221.
Ma H, Nguyen C, Lee KS, Kahn M . (2005). Differential roles for the coactivators CBP and p300 on TCF/beta-catenin-mediated survivin gene expression. Oncogene 24: 3619–3631.
Matteucci E, Modora S, Simone M, Desiderio MA . (2003). Hepatocyte growth factor induces apoptosis through the extrinsic pathway in hepatoma cells: favouring role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 deficiency. Oncogene 22: 4062–4073.
Monga SP, Mars WM, Pediaditakis P, Bell A, Mule K, Bowen WC et al. (2002). Hepatocyte growth factor induces Wnt-independent nuclear translocation of beta-catenin after Met-beta-catenin dissociation in hepatocytes. Cancer Res 62: 2064–2071.
Ougolkov A, Zhang B, Yamashita K, Bilim V, Mai M, Fuchs SY et al. (2004). Associations among beta-TrCP, an E3 ubiquitin ligase receptor, beta-catenin, and NF-kappaB in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96: 1161–1170.
Papkoff J, Aikawa M . (1998). WNT-1 and HGF regulate GSK3 beta activity and beta-catenin signaling in mammary epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247: 851–858.
Radtke F, Clevers H . (2005). Self-renewal and cancer of the gut: two sides of a coin. Science 307: 1904–1909.
Rasola A, Anguissola S, Ferrero N, Gramaglia D, Maffe A, Maggiora P et al. (2004). Hepatocyte growth factor sensitizes human ovarian carcinoma cell lines to paclitaxel and cisplatin. Cancer Res 64: 1744–1750.
Rasola A, Geuna M . (2001). A flow cytometry assay simultaneously detects independent apoptotic parameters. Cytometry 45: 151–157.
Reya T, Clevers H . (2005). Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 434: 843–850.
Rowan AJ, Lamlum H, Ilyas M, Wheeler J, Straub J, Papadopoulou A et al. (2000). APC mutations in sporadic colorectal tumors: a mutational ‘hotspot’ and interdependence of the ‘two hits’. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 3352–3357.
Sancho E, Batlle E, Clevers H . (2004). Signaling pathways in intestinal development and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20: 695–723.
Takeuchi H, Bilchik A, Saha S, Turner R, Wiese D, Tanaka M et al. (2003). c-MET expression level in primary colon cancer: a predictor of tumor invasion and lymph node metastases. Clin Cancer Res 9: 1480–1488.
Trusolino L, Comoglio PM . (2002). Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: cell signalling for invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 289–300.
van Es JH, Barker N, Clevers H . (2003). You Wnt some, you lose some: oncogenes in the Wnt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13: 28–33.
van Gijn ME, Snel F, Cleutjens JP, Smits JF, Blankesteijn WM . (2001). Overexpression of components of the Frizzled–Dishevelled cascade results in apoptotic cell death, mediated by beta-catenin. Exp Cell Res 265: 46–53.
Vigna E, Naldini L . (2000). Lentiviral vectors: excellent tools for experimental gene transfer and promising candidates for gene therapy. J Gene Med 2: 308–316.
Wielenga VJ, van der Voort R, Taher TE, Smit L, Beuling EA, van Krimpen C et al. (2000). Expression of c-Met and heparan-sulfate proteoglycan forms of CD44 in colorectal cancer. Am J Pathol 157: 1563–1573.
Zeng Q, Chen S, You Z, Yang F, Carey TE, Saims D et al. (2002). Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits anoikis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by activation of ERK and Akt signaling independent of NFkappa B. J Biol Chem 277: 25203–25208.
Acknowledgements
We thank Raffaella Albano, Laura Palmas and Solange Tienga for technical assistance. We are deeply indebted to Dr Federica Chiara, Dr Tiziana Venesio and Dr Daniela Cimino for helpful discussion, to Dr Ivan Dmitriev and Dr Damion Milne for the development and setup of the Image Analyzer software, and to our system operators Mario Belluardo, Antonino Ferraro, Andrea Carena and Paola Mantovani for inexhaustible support. Professor B Vogelstein gently provided the human β-catenin plasmid, Professor K Berns the β-catenin siRNAs, Dr S Corso the HGFR siRNAs and Dr G Nolan the Phoenix cell line.This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Research and Education (FIRB/MIUR), by the Italian National Research Council (CNR – MIUR Progetto Oncologia) and by the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC) funding to PMC and MFDR. AR and MF are recipient of Regione Piemonte Ricerca Scientifica Applicata fellowships. LDA is recipient of Italian Federation for Basic Research (FIRB) fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasola, A., Fassetta, M., De Bacco, F. et al. A positive feedback loop between hepatocyte growth factor receptor and β-catenin sustains colorectal cancer cell invasive growth. Oncogene 26, 1078–1087 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209859
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209859
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) in cancer
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2018)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: FOXC2 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by directly targeting MET
Oncogene (2015)
-
Signaling cross-talk in the resistance to HER family receptor targeted therapy
Oncogene (2014)
-
Combined analysis of KRAS and PIK3CA mutations, MET and PTEN expression in primary tumors and corresponding metastases in colorectal cancer
Modern Pathology (2013)
-
Mechanisms of RAS/β-catenin interactions
Archives of Toxicology (2013)