Abstract
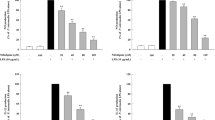
The immediate-early cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) gene encodes an inducible prostaglandin synthase enzyme which is implicated in inflammatory and proliferative diseases. COX-2 is highly induced during cell activation by various factors, including mitogens, hormones and cytokines. Since pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β has been shown to induce prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) release in human gingival fibroblasts (HGF), here we analyzed the effect of IL-1β on the expression of COX-2 and the activation of NFκB in HGF. Northern hybridization analysis revealed that IL-1β (200 pg/ml) increased the expression of COX-2 mRNA in HGF. The effect of IL-1β was abrogated by herbimycin A, a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and enhanced by orthovanadate, a protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. IL-1β-induced PGE2 release was blocked by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor and increased by the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. The results of transient transfection assays using chimeric constructs of the human COX-2 promoter (nt -1432 ~ +59) ligated to a luciferase reporter gene indicated that IL-1β stimulated the transcriptional activity ~ 1.5-fold. Gel mobility shift assays with a radiolabelled COX-2-NFκB oligonucleotide (nts -223 to -214) revealed an increase in the binding of nuclear proteins from IL-1β-stimulated HGF. This increase of DNA-protein complex formation induced by IL-1β was blocked by herbimycin A and another tyrosine kinase inhibitor, genistein. These results suggest that NFκB is an important transcription factor for IL-1β-induced COX-2 gene expression, and is involved in inducing COX-2 gene transcription through tyrosine phosphorylation in HGF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng L, Sun W, Xia Y, Tang WW, Chanmugam P, Soyoola E, Wilson C, Hwang D: Cloning two isoforms of rat cyclooxygenase: Differential regulation of their expression. Arch Biochem Biophys 307: 361-368, 1993
Inoue H, Nanayama T, Hara S, Yokoyama C, Tanabe T: The cyclic AMP response element plays an essential role in the expression of the human prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 gene in differentiated U937 monocytic cells. FEBS Lett 350: 51-54, 1994
Kosaka T, Miyata A, Ihara H, Hara S, Sugimoto T, Takeda O, Takahashi E, Tanabe T: Characterization of the human gene (PTGS2) encoding prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2. Eur J Biochem 221: 889-897, 1994
Roshak AK, Jackson JR, Mcgough K, Chabot-Fletcher M, Mochan E, Marshall LA: Manipulation of distinct NFκB proteins alters interleukin-1β-induced human rheumatoid synovial fibroblast prostaglandin E2 formation. J Biol Chem 271: 31496-31501, 1996
Inoue H, Yokoyama C, Hara S, Tone Y, Tanabe T: Transcriptional regulation of human prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase-2 gene by lipopolysaccharide and phorbol ester in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 270: 24965-24971, 1995
Chen QR, Miyaura C, Higashi S, Murakami M, Kudo I, Saito S, Hiraide T, Shibasaki Y, Suda T: Activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by platelet-derived growth factor is essential for cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin E2 synthesis in mouse osteoblasts cultured with interleukin-1. J Biol Chem 272: 5952-5958, 1997
Yamamoto K, Arakawa T, Ueda N, Yamamoto S: Transcriptional roles of nuclear factor κB and nuclear factor-interleukin-6 in the tumor necrosis factor α-dependent induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in MC3T3-E1 cells. J Biol Chem 270: 31315-31320, 1995
Xie W, Herschman HR: Transcriptional regulation of prostaglandin synthase 2 gene expression by platelet-derived growth factor and serum. J Biol Chem 271: 31742-31748, 1996
Yokota Y, Niisato N, Ogata Y, Moriwaki K, Furuyama S, Sugiya H: Bradykinin stimulates Ca2+ release from inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate sensitive pool, which is insufficient for prostaglandin E2 release in human gingival fibroblasts. Biomed Res 15: 391-397, 1994
Niisato N, Ogata Y, Furuyama S, Sugiya H: Histamine H1 receptorinduced Ca2+ mobilization and prostaglandin E2 release in human gingival fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol 52: 1015-1023, 1996
Offenbacher S, Farr DH, Goodson JM: Measurement of prostaglandin E in crevicular fluid. J Clin Periodontol 8: 359-367, 1981
Yucel-Lindberg T, Ahola H, Nilsson S, Carlstedt-Duke J, Modéer T: Interleukin-1β induces expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in human gingival fibroblasts. Inflammation 19: 549-560, 1995
Nakao S, Moriya Y, Ogata Y, Furuyama S, Sugiya H: Bradykinin amplifies IL-1β-induced expression of COX-2 in gingival fibroblasts. J Dent Res 76: (abstr) 110, 1997.
Somerman MJ, Archer SY, Imm GR, Foster RA: A comparative study of human periodontal ligament cell and gingival fibroblasts in vitro. J Dent Res 67: 66-70, 1988
Ogata Y, Niisato N, Sakurai T, Furuyama S, Sugiya H: Comparison of the characteristics of human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontol 66: 1025-1031, 1995
Ogata Y, Niisato N, Furuyama S, Cheifetz S, Kim RH, Sugiya H, Sodek J: Transforming growth factor-β1 regulation of bone sialoprotein gene transcription: Identification of a TGF-β activation element in the rat BSP gene promoter. J Cell Biochem 65: 501-512, 1997
Rose JK, Buonocore L, Whitt MA: A new cationic liposome reagent mediating nearly quantitative transfection of animal cells. Biotechniques 10: 520-525, 1991
Dignam JD, Lebovitz RM, Roeder RG: Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucl Acids Res 11: 1475-1489, 1983
Belt A, Baldassare JJ, Molnar M, Romero R, Hertelendy F: The nuclear transcription factor NF-κB mediates interleukin-1β-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human myometrial cells. Am J Obstet Gynecol 181: 359-366, 1999
Wang Z, Tai HH: Interleukin-1β and dexamethasone regulate gene expression of prostaglandin H synthase-2 via the NF-κB pathway in human amnion derived WISH cells. Prostagland Leuk Essen Fatty Acids 59: 63-69, 1998
Newton R, Stevens DA, Hart LA, Lindsay M, Adcock IM, Barnes PJ: Superinduction of COX-2 mRNA by cycloheximide and interleukin-1β involves increased transcription and correlates with increased NFκB and JNK activation. FEBS Lett 418: 135-138, 1997
Newton R, Kuitert LME, Bergmann M, Adcock IM, Barnes PJ: Evidence for involvement of NF-κB in the transcriptional control of COX-2 gene expression by IL-1β. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 237: 28-32, 1997
Crofford LJ, Tan B, McCarthy CJ, Hla T: Involvement of nuclear factor κB in the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by interleukin-1 in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Arth Rheum 40: 226-236, 1997
Yucel-Lindberg T, Ahola H, Carlstedt-Duke J, Modéer T: Involvement of tyrosine kinases on cyclooxygenase expression and prostaglandin E2 production in human gingival fibroblasts stimulated with interleukin-1β and epidermal growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257: 528-532, 1999
Natarajan K, Manna SK, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB: Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors block tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of nuclear factor-κB, degradation of IκBα, nuclear translocation of p65, and subsequent gene expression. Arch Biochem Biophys 352: 59-70, 1998
Baldwin AS: The NF-κB and IκB proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14: 649-683, 1996
Mahon TM, O'Neill LA: Studies into the effect of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor herbimycin A on NF-κB activation in T lymphocytes. Evidence for covalent modification of the p50 subunit. J Biol Chem 270: 28557-28564, 1995
Tetsuka T, Srivastava SK, Morrison AR: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors, genistein and herbimycin A, do not block interleukin-1β-induced activation of NFκB in rat mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 218: 808-812, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakao, S., Ogata, Y., Shimizu-Sasaki, E. et al. Activation of NFκB is necessary for IL-1β-induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in human gingival fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem 209, 113–118 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007155525020
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007155525020