Abstract
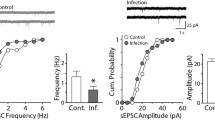
Viral infections of the central nervous system (CNS) are associated with an increased risk for seizures during the acute infection period and the subsequent development of chronic epilepsy that is often difficult to treat. In previous work, we have shown that mice of the C57BL/6 strain infected with Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV) exhibit a similar sequence, thereby providing a potential useful model of virus-induced epilepsy. The present study examines spontaneous and miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in CA3 pyramidal cells recorded from brain slices prepared during both the acute phase during encephalitis and 2 months following TMEV infection. Animals that develop chronic epilepsy following TMEV infection exhibit considerable hippocampal sclerosis, directly implicating this brain region in the process of epileptogenesis. There are significant increases in amplitude and frequency of spontaneous and miniature excitatory currents in CA3 cells recorded in brain slices prepared during the acute infection period and 2 months after infection. However, the patterns of changes observed are markedly different during these two periods, suggesting that there are underlying changes in the network over time. These differences have implications for the treatment used during the acute infection and after chronic seizures develop.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson WW, Swartzwelder HS, Wilson WA (1987) The NMDA receptor antagonist 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate blocks stimulus train-induced epileptogenesis but not epileptiform bursting in the rat hippocampal slice. J Neurophysiol 57:1–21
Annegers JF, Hauser WA, Beghi E, Nicolosi A, Kurland LT (1988) The risk of unprovoked seizures after encephalitis and meningitis. Neurology 38:1407–1410
Bains JS, Longacher JM, Staley KJ (1999) Reciprocal interactions between CA3 network activity and strength of recurrent collateral synapses. Nat Neurosci 2:720–726
Beers DR, Henkel JS, Schaefer DC, Rose JW, Stroop WG (1993) Neuropathology of herpes simplex virus encephalitis in a rat seizure model. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52:241–252
Ben-Ari Y, Gho M (1988) Long-lasting modification of the synaptic properties of rat CA3 hippocampal neurones induced by kainic acid. J Physiol 404:365–384
Blanton MG, Lo Turco JJ, Kriegstein AR (1989) Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Methods 30:203–210
Buzsaki G (1986) Hippocampal sharp waves: their origin and significance. Brain Res 398:242–252
Chamberlin NL, Traub RD, Dingledine R (1990) Role of EPSPs in initiation of spontaneous synchronized burst firing in rat hippocampal neurons bathed in high potassium. J Neurophysiol 64:1000–1008
Chen SF, Huang CC, Wu HM, Chen SH, Liang YC, Hsu KS (2004) Seizure, neuron loss, and mossy fiber sprouting in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected organotypic hippocampal cultures. Epilepsia 45:322–332
Congar P, Gaiarsa JL, Popovici T, Ben-Ari Y, Crepel V (2000) Permanent reduction of seizure threshold in post-ischemic CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 83:2040–2046
Dzhala VI, Staley KJ (2003) Transition from interictal to ictal activity in limbic networks in vitro. J Neurosci 23:7873–7880
Eeg-Olofsson O (2003) Virological and immunological aspects of seizure disorders. Brain Dev 25:9–13
Eisenschenk SGR (2000) Seizures associated with non- neurological medical conditions. In: Wyllie E (ed) The treatment of epilepsy: principles and practice. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Co., New York, pp 657–669
Epsztein J, Milh M, Bihi RI, Jorquera I, Ben-Ari Y, Represa A, Crepel V (2006) Ongoing epileptiform activity in the post-ischemic hippocampus is associated with a permanent shift of the excitatory-inhibitory synaptic balance in CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 26:7082–7092
Epsztein J, Ben-Ari Y, Represa A, Crepel V (2008) Late-onset epileptogenesis and seizure genesis: lessons from models of cerebral ischemia. Neuroscientist 14:78–90
Esclapez M, Hirsch JC, Ben-Ari Y, Bernard C (1999) Newly formed excitatory pathways provide a substrate for hyperexcitability in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. J Comp Neurol 408:449–460
Getts DR, Matsumoto I, Muller M, Getts MT, Radford J, Shrestha B, Campbell IL, King NJ (2007) Role of IFN-gamma in an experimental murine model of West Nile virus-induced seizures. J Neurochem 103:1019–1030
Getts DR, Balcar VJ, Matsumoto I, Muller M, King NJ (2008) Viruses and the immune system: their roles in seizure cascade development. J Neurochem 104:1167–1176
Gilbert M, Racine RJ, Smith GK (1985) Epileptiform burst responses in ventral vs dorsal hippocampal slices. Brain Res 361:389–391
Gomez-Di Cesare CM, Smith KL, Rice FL, Swann JW (1997) Axonal remodeling during postnatal maturation of CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Comp Neurol 384:165–180
Goodman SN (1999) Toward evidence-based medical statistics. 1: The P value fallacy. Ann Intern Med 130:995–1004
Griffith JF, Kibrick S, Dodge PR, Richardson EP (1967) Experimental herpes simplex encephalitis. Electroencephalographic, clinical, virologic, and pathologic observations in the rabbit. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 23:263–269
Hablitz JJ (1984) Picrotoxin-induced epileptiform activity in hippocampus: role of endogenous versus synaptic factors. J Neurophysiol 51:1011–1027
Hellier JL, White A, Williams PA, Edward Dudek F, Staley KJ (2009) NMDA receptor-mediated long-term alterations in epileptiform activity in experimental chronic epilepsy. Neuropharmacology 56:414–421
Henze DA, Card JP, Barrionuevo G, Ben-Ari Y (1997) Large amplitude miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons are of mossy fiber origin. J Neurophysiol 77:1075–1086
Hunsperger EA, Roehrig JT (2006) Temporal analyses of the neuropathogenesis of a West Nile virus infection in mice. J Neurovirol 12:129–139
Kirkman NJ, Libbey JE, Wilcox KS, White HS, Fujinami RS (2010) Innate but not adaptive immune responses contribute to behavioral seizures following viral infection. Epilepsia 51:454–464
Klein BD, Fu YH, Ptacek LJ, White HS (2004) c-Fos immunohistochemical mapping of the audiogenic seizure network and tonotopic neuronal hyperexcitability in the inferior colliculus of the Frings mouse. Epilepsy Res 62:13–25
Labar DR, Harden C (1998) Infection and inflammatory diseases. In: Engel J Jr, Pedley TA (eds) Epilepsy: a comprehensive textbook. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, New York, pp 2587–2596
Lehrmann E, Guidetti P, Love A, Williamson J, Bertram EH, Schwarcz R (2008) Glial activation precedes seizures and hippocampal neurodegeneration in measles virus-infected mice. Epilepsia 49(Suppl 2):13–23
Libbey JE, Kirkman NJ, Smith MC, Tanaka T, Wilcox KS, White HS, Fujinami RS (2008) Seizures following picornavirus infection. Epilepsia 49:1066–1074
Lothman EW (1994) Seizure circuits in the hippocampus and associated structures. Hippocampus 4:286–290
MacVicar BA, Dudek FE (1980) Local synaptic circuits in rat hippocampus: interactions between pyramidal cells. Brain Res 184:220–223
McNamara JO (1994) Cellular and molecular basis of epilepsy. J Neurosci 14:3413–3425
Misra UK, Tan CT, Kalita J (2008) Viral encephalitis and epilepsy. Epilepsia 49(Suppl 6):13–18
Oliver AP, Carman JS, Hoffer BJ, Wyatt RJ (1980) Effect of altered calcium ion concentration on interictal spike generation in the hippocampal slice. Exp Neurol 68:489–499
Schmutzhard E (2001) Viral infections of the CNS with special emphasis on herpes simplex infections. J Neurol 248:469–477
Schwartzkroin PA, Prince DA (1977) Penicillin-induced epileptiform activity in the hippocampal in vitro prepatation. Ann Neurol 1:463–469
Shao LR, Dudek FE (2004) Increased excitatory synaptic activity and local connectivity of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells in rats with kainate-induced epilepsy. J Neurophysiol 92:1366–1373
Shao LR, Dudek FE (2009) Both synaptic and intrinsic mechanisms underlie the different properties of population bursts in the hippocampal CA3 area of immature versus adult rats. J Physiol 587:5907–5923
Solbrig MV (2010) Animal models of CNS viral disease: examples from borna disease virus models. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis 2010:709791
Solbrig MV, Adrian R, Baratta J, Lauterborn JC, Koob GF (2006) Kappa opioid control of seizures produced by a virus in an animal model. Brain 129:642–654
Stasheff SF, Anderson WW, Clark S, Wilson WA (1989) NMDA antagonists differentiate epileptogenesis from seizure expression in an in vitro model. Science 245:648–651
Stellwagen D, Malenka RC (2006) Synaptic scaling mediated by glial TNF-alpha. Nature 440:1054–1059
Stellwagen D, Beattie EC, Seo JY, Malenka RC (2005) Differential regulation of AMPA receptor and GABA receptor trafficking by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Neurosci 25:3219–3228
Stewart KA, Wilcox KS, Fujinami RS, White HS (2010a) Development of postinfection epilepsy after Theiler's virus infection of C57BL/6 mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:1210–1219
Stewart KA, Wilcox KS, Fujinami RS, White HS (2010b) Theiler's virus infection chronically alters seizure susceptibility. Epilepsia 51:1418–1428
Stringer JL (2006) Models available for infection-induced seizures. In: Pitkanen A, Schwartzkroin PA, Moshe SL (eds) Models of seizures and epilepsy. Elsevier Academic Press, New York, pp 521–526
Traub RD, Wong RK (1982) Cellular mechanism of neuronal synchronization in epilepsy. Science 216:745–747
Wong RK, Traub RD (1983) Synchronized burst discharge in disinhibited hippocampal slice. I. Initiation in CA2-CA3 region. J Neurophysiol 49:442–458
Wu HM, Huang CC, Chen SH, Liang YC, Tsai JJ, Hsieh CL, Hsu KS (2003) Herpes simplex virus type 1 inoculation enhances hippocampal excitability and seizure susceptibility in mice. Eur J Neurosci 18:3294–3304
Wuarin JP, Dudek FE (2001) Excitatory synaptic input to granule cells increases with time after kainate treatment. J Neurophysiol 85:1067–1077
Yamashita N, Morishima T (2005) HHV-6 and seizures. Herpes 12:46–49
Ylinen A, Bragin A, Nadasdy Z, Jando G, Szabo I, Sik A, Buzsaki G (1995) Sharp wave-associated high-frequency oscillation (200 Hz) in the intact hippocampus: network and intracellular mechanisms. J Neurosci 15:30–46
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of Robert and Joyce Rice (Salt Lake City, UT), the Margolis Foundation (Salt Lake City, UT), Citizens United for Research in Epilepsy (HSW and RSF), National Institutes of Health 1R01NS065714 (RSF), the Epilepsy Foundation (KAS), and the American Epilepsy Society (KAS), the Dumke Foundation (KSW) and National Institutes of Health R21 NS41673 (KSW). We would also like to thank Dr. Alla Borisyuk for advice about data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smeal, R.M., Stewart, KA., Iacob, E. et al. The activity within the CA3 excitatory network during Theiler's virus encephalitis is distinct from that observed during chronic epilepsy. J. Neurovirol. 18, 30–44 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-012-0082-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-012-0082-5