Abstract
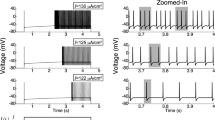
Mitral cells, the principal output neurons of the olfactory bulb, receive direct synaptic activation from primary sensory neurons. Shunting inhibitory inputs delivered by granule cell interneurons onto mitral cell lateral dendrites, while poorly positioned to prevent spike initiation, are believed to influence spike timing and underlie coordinated field potential oscillations. We investigated this phenomenon in a reduced compartmental mitral cell model suitable for incorporation into network simulations. Lateral dendritic shunt conductances delayed spiking to a degree dependent on both their electrotonic distance and phase of onset. Moreover, when the afferent activation of mitral cells was loosely coordinated in time, recurrent inhibition significantly narrowed the distribution of mitral cell spike times, illustrating a tendency towards coordinated synchronous activity. However, if mitral cell activity was initially disorganized, recurrent inhibition actually increased the variance in spike timing. This result suggests an essential role for early mechanisms of temporal coordination in olfaction, such as sniffing and the initial synchronization of mitral cell intrinsic oscillations by periglomerular cell-mediated inhibition.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton, P. S., Granger, R., & Lynch, G. (1993). Simulated dendritic spines influence reciprocal synaptic strengths and lateral inhibition in the olfactory bulb. Brain Research, 628, 157–165.
Aungst, J. L., Heyward, P. M., Puche, A. C., Karnup, S. V., Hayar, A., Szabo, G., et al. (2003). Centre-surround inhibition among olfactory bulb glomeruli. Nature, 426, 623–629.
Balu, R., Pressler, R. T., & Strowbridge, B. W. (2007). Multiple modes of synaptic excitation of olfactory bulb granule cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 5621–5632.
Bathellier, B., Lagier, S., Faure, P., & Lledo, P. M. (2006). Circuit properties generating gamma oscillations in a network model of the olfactory bulb. Journal of Neurophysiology, 95, 2678–2691.
Bhalla, U. S., & Bower, J. M. (1993). Exploring parameter space in detailed single neuron models: simulations of the mitral and granule cells of the olfactory bulb. Journal of Neurophysiology, 69, 1948–1965.
Brody, C. D., & Hopfield, J. J. (2003). Simple networks for spike-timing-based computation, with application to olfactory processing. Neuron, 37, 843–852.
Cang, J., & Isaacson, J. S. (2003). In vivo whole-cell recording of odor-evoked synaptic transmission in the rat olfactory bulb. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 4108–4116.
Chen, W. R., Shen, G. Y., Shepherd, G. M., Hines, M. L., & Midtgaard, J. (2002). Multiple modes of action potential initiation and propagation in mitral cell primary dendrite. Journal of Neurophysiology, 88, 2755–2764.
Cleland, T. A., & Linster, C. (2002). How synchronization properties among second-order sensory neurons can mediate stimulus salience. Behavioral Neuroscience, 116, 212–221.
Cleland, T. A., & Linster, C. (2005). Computation in the olfactory system. Chemical Senses, 30, 801–813.
Cleland, T. A., & Sethupathy, P. (2006). Non-topographical contrast enhancement in the olfactory bulb. BMC Neuroscience, 7, 7.
Davison, A. P., Feng, J., & Brown, D. (2000). A reduced compartmental model of the mitral cell for use in network models of the olfactory bulb. Brain Research Bulletin, 51, 393–399.
Davison, A. P., Feng, J., & Brown, D. (2003). Dendrodendritic inhibition and simulated odor responses in a detailed olfactory bulb network model. Journal of Neurophysiology, 90, 1921–1935.
Debarbieux, F., Audinat, E., & Charpak, S. (2003). Action potential propagation in dendrites of rat mitral cells in vivo. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 5553–5560.
Desmaisons, D., Vincent, J. D., & Lledo, P. M. (1999). Control of action potential timing by intrinsic subthreshold oscillations in olfactory bulb output neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 19, 10727–10737.
Eeckman, F. H., & Freeman, W. J. (1990). Correlations between unit firing and EEG in the rat olfactory system. Brain Research, 528, 238–244.
Egger, V., Svoboda, K., & Mainen, Z. F. (2003). Mechanisms of lateral inhibition in the olfactory bulb: efficiency and modulation of spike-evoked calcium influx into granule cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 7551–7558.
Egger, V., Svoboda, K., & Mainen, Z. F. (2005). Dendrodendritic synaptic signals in olfactory bulb granule cells: Local spine boost and global low-threshold spike. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 3521–3530.
Galan, R. F., Ermentrout, G. B., & Urban, N. N. (2005). Efficient estimation of phase-resetting curves in real neurons and its significance for neural-network modeling. Physical Review Letter, 94, 158101.
Galan, R. F., Fourcaud-Trocme, N., Ermentrout, G. B., & Urban, N. N. (2006). Correlation-induced synchronization of oscillations in olfactory bulb neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 3646–3655.
Jahr, C. E., & Nicoll, R. A. (1982). An intracellular analysis of dendrodendritic inhibition in the turtle in vitro olfactory bulb. Journal of Physiology, 326, 213–234.
Lagier, S., Carleton, A., & Lledo, P. M. (2004). Interplay between local GABAergic interneurons and relay neurons generates gamma oscillations in the rat olfactory bulb. Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 4382–4392.
Laurent, G. (2002). Olfactory network dynamics and the coding of multidimensional signals. Nature Reviews, Neuroscience, 3, 884–895.
Lestienne, R., Tuckwell, H. C., Chalansonnet, M., & Chaput, M. (1999). Repeating triplets of spikes and oscillations in the mitral cell discharges of freely breathing rats. European Journal of Neuroscience, 11, 3185–3193.
Li, Z. (1990). A model of olfactory adaptation and sensitivity enhancement in the olfactory bulb. Biological Cybernetics, 62, 349–361.
Li, Z., & Hopfield, J. J. (1989). Modeling the olfactory bulb and its neural oscillatory processings. Biological Cybernetics, 61, 379–392.
Linster, C., & Gervais, R. (1996). Investigation of the role of interneurons and their modulation by centrifugal fibers in a neural model of the olfactory bulb. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 3, 225–246.
Linster, C., & Hasselmo, M. (1997). Modulation of inhibition in a model of olfactory bulb reduces overlap in the neural representation of olfactory stimuli. Behavioral Brain Research, 84, 117–127.
Lowe, G. (2003). Flash photolysis reveals a diversity of ionotropic glutamate receptors on the mitral cell somatodendritic membrane. Journal of Neurophysiology, 90, 1737–1746.
Margrie, T. W., & Schaefer, A. T. (2003). Theta oscillation coupled spike latencies yield computational vigour in a mammalian sensory system. Journal of Physiology, 546, 363–374.
Migliore, M., Hines, M. L., & Shepherd, G. M. (2005). The role of distal dendritic gap junctions in synchronization of mitral cell axonal output. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 18, 151–161.
Nusser, Z., Kay, L. M., Laurent, G., Homanics, G. E., & Mody, I. (2001). Disruption of GABA(A) receptors on GABAergic interneurons leads to increased oscillatory power in the olfactory bulb network. Journal of Neurophysiology, 86, 2823–2833.
Pressler, R. T., & Strowbridge, B. W. (2006). Blanes cells mediate persistent feedforward inhibition onto granule cells in the olfactory bulb. Neuron, 49, 889–904.
Rall, W., & Shepherd, G. M. (1968). Theoretical reconstruction of field potentials and dendrodendritic synaptic interactions in olfactory bulb. Journal of Neurophysiology, 31, 884–915.
Rinberg, D., Koulakov, A., & Gelperin, A. (2006). Sparse odor coding in awake behaving mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 8857–8865.
Rubin, D. B., & Cleland, T. A. (2006). Dynamical mechanisms of odor processing in olfactory bulb mitral cells. Journal of Neurophysiology, 96, 555–568.
Schoppa, N. E. (2006a). AMPA/kainate receptors drive rapid output and precise synchrony in olfactory bulb granule cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 12996–13006.
Schoppa, N. E. (2006b). Synchronization of olfactory bulb mitral cells by precisely timed inhibitory inputs. Neuron, 49, 271–283.
Schoppa, N. E., Kinzie, J. M., Sahara, Y., Segerson, T. P., & Westbrook, G. L. (1998). Dendrodendritic inhibition in the olfactory bulb is driven by NMDA receptors. Journal of Neuroscience, 18, 6790–6802.
Usrey, W. M., Alonso, J. M., & Reid, R. C. (2000). Synaptic interactions between thalamic inputs to simple cells in cat visual cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 20, 5461–5467.
Zelles, T., Boyd, J. D., Hardy, A. B., & Delaney, K. R. (2006). Branch-specific Ca2+ influx from Na+-dependent dendritic spikes in olfactory granule cells. Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 30–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Action Editor: James M. Bower
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
David, F., Linster, C. & Cleland, T.A. Lateral dendritic shunt inhibition can regularize mitral cell spike patterning. J Comput Neurosci 25, 25–38 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-007-0063-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-007-0063-5