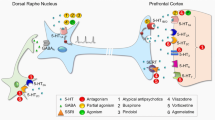
Abstract
Individualized medicine through molecular pharmacogenetics is one of the major future goals in clinical medicine. In psychopharmacology, pharmacogenetics became an expanding research component. Major research results were already attained: first, it is now feasible to predict a major proportion of the interindividual variation of plasma levels of most antidepressants and antipsychotics by using the DNA-sequence variation in genes for crucial CYP P450-enzymes as CYP2D6. Second, it is now possible to relate serious side effects (tardive dyskinesia, weight gain) of antipsychotics to specific genetic variants of genes for target proteins. Third, a long list of mainly functional variants in target protein genes was explored for their predictive power for the beneficial and adverse treatment outcome. Although specific results transferable into clinical practice were not yet obtained in this respect, the proof of principle could be demonstrated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arranz MJ, Munro J, Sham P, Kirov G, Murray RM, Collier DA, Kerwin RW (1998) Meta-analysis of studies on genetic variation in 5-Ht2A receptors and clozapine response. Schizophr Res 32(2):93–99
Arranz MJ, Munro J, Birkett J, Bolonna A, Mancama D, Sodhi M, Lesch KP, Meyer JF, Sham P, Collier DA, Murray RM, Kerwin RW (2000) Pharmacogenetic prediction of clozapine response. Lancet 355(9215):1615–1616
Arranz MJ, de Leon J (2007) Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics of schizophrenia: a rview of last decade of research. Mol Psychiatry 12(8):707–747
Basile VS, Ozdemir V, Masellis M, Meltzer HY, Lieberman JA, Potkin SG, Macciardi FM, Kennedy JL (2001), Lack of association between serotonin-2A receptor gene (HTR2A) polymorphisms: tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 6:230–234
Binder EB, Holsboer F (2006), Pharmacogenomics and antidepressant drugs. Ann Med 38:82–94
Brockmoller J, Kirchhainer J, Schmider J, Walter S, Sachse C, Muller-Oerlinghausen B et al (2002) The impact of the CYP2D6 polymorphism on haloperidol pharmacokinetics and on the outcome of haloperidol treatment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:438–452
Brosen K, Naranjo CA (2001) Review of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interaction studies with citalopram. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:275–283
Chou WH, Yan FX, Robbins-Weilert DK, Ryder TB, Liu WW, Perbost C, Fairchild M, de Leon J, Koch WH, Wedlung PJ (2003) Comparison of two CYP2D6 genotyping methods and assessment of genotype–phenotype relationships. Clin Chem 49(4):542–551
Collins FS (1999) Shattuck lecture—medical and societal consequences of the Human Genome Project. N Engl J Med 341(1):28–37
Cusin C, Serretti A, Zanardi R, Lattuada E, Rossini D, Lilli R, Lorenzi C, Smeraldi E (2002) Influence of monoamine oxidase A and serotonin receptor 2A polymorphisms in SSRI antidepressant activity. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 5(1):27–35
Dahl ML (2002) Cytochrome P450 phenotyping/genotyping in patients receiving antipsychotics: useful aid to prescribing? Clin Pharmacokinet 41:453–470
de Leon J, Armstrong SC, Cozza KL (2006) Clinical guidelines for psychiatrists for the use of pharmacogenetic testing for CYP450 2D6 and CYP450 2C19. Psychosomatics 47(1):75–85
Durham LK, Webb SM, Milos PM, Clary CM, Seymour AB (2004) The serotonin transporter polymorphism, 5HTTLPR, is associated with a faster response time to sertraline in an elderly population with major depressive disorder. Psychopharmacology 174(4):525–529
Emsley RA, Roberts MC, Rataemane S, Pretorius J, Oosthuizen PP, Turner J, Niehaus DJ, KeyterN, Stein DJ (2002) Ethnicity and treatment response in schizophrenia: a comparison of 3 ethnic groups. J Clin Psychiatry 63(1):9–14
Evans WE, Relling MV (1999) Pharmacogenomics: translating functional genomics into rational therapeutics. Science 286(5439):487–491
Grasmäder K, Vewohlt PL, Kühn KU, Dragicevic A, von Widdern O, Zobel A, Hiemke C, Rietschel M, Maier W, Jaehde U, Rao ML (2004a) Population pharmacokinetic analysis of mirtazapine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60(7):473–480
Grasmäder K, Vewohlt PL, Rietschel M, Dragicevic A, Müller M, Hiemke C, Freymann N, Zobel A, Maier W, Rao ML (2004b) Impact of polymorphisms of cytochrome-P450 isoenzymes 2C9, 2C19 and 2D6 on plasma concentrations and clinical effects of antidepressants in a naturalistic clinical setting. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60:329–336
Hong CF, Lin CH, Yu YWY, Yang KH, Tsai SJ (2001) Genetic variants of the serotonin system and weight change during clozapine treatment. Pharmacogenetics 11:265–268
Hu X-Z, Lipsky RH, Zhu G, Akhtar LA, Taubman J, Greenberg BD, Xu K, Arnold PD, Richter MA, Kennedy JL, Murphy DL, Goldman D (2006) Serotonin transporter promoter gain-of-function genotypes are linked to obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Hum Genet 78:815–826
Hu X-Z, Rush AJ, Charney D, Wilson AF, Sorant AJM, Papanicolaou GJ, Fava M, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Laje G, Paccock S, McMahon FJ, Manji H, Lipsky RH (2007) Association between a functional serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism and Citalopram treatment in adult outpatients with major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64(7):783–792
Ingelman-Sundberg M (2004) Pharmacogenetics of cytochrome P450 and its applications in drug therapy: the past, present and future. Trend Pharmacol Sci 25(4):193–200
Ingelman-Sundberg M (2005) Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 (CYP2D6): clinical consequences, evolutionary aspects and functional diversity. Pharmacogenomics 5(1):6–13
Jonsson EG, Nothen MM, Grunhage F, Farde L, Nakashima Y, Propping P, Sedvall GC (1999) Polymorphisms in the dopamine D2 receptor gene and their relationships to striatal dopamine receptor density of healthy volunteers. Mol Psychiatry 4:290–296
Kirchhainer J, Nickchen K, Bauer M, Wong M-L, Licinio J, Roots I, Brockmöller J (2004) Pharmacogenetics of antidepressants and antipsychotics: the contribution of allelic variations to the phenotype of drug response. Mol Psychiatry 9:442–473
Kraft JB, Slager SL, McGrath PJ, Hamilton SP (2005) Sequence analysis of the serotonin transporter and associations with antidepressant response. Biol Psychiatry 58(5):374–381
Lencz T, Robinson DG, Xu K, Ekholm J, Sevy S, Gunduz-Bruce H, Woerner MG, Kane JM, Goldman D, Malhotra AK (2006) DRD2 promoter region variation as a predictor of sustained response to antipsychotic medication in first-episode schizophrenia patients. Am J Psychiatry 163:529–531
Lerer B, Segman RH, Fangerau H, Daly AK, Basile VS, Cavallaro R, Aschauer HN, McCreadie RG, Ohlraun S, Ferrier N, Masellis M, Verga M, Scharfetter J, Rietschel M, Lovlie R, Levy UH, Meltzer HY, Kenney JL, Steen VM, Macciardi F (2002) Pharmacogenetics of tardive dyskinesia: comined analysis of 780 patients supports association with dopamine d3 receptor gene Ser9Gly polymorphism. Neuropsychopharmacology 27(1):105–119
Lundstrom K, Turpin MP (1996) Proposed schizophrenia-related gene polymorphis: expression of the Ser9Gly mutant human dopanie D3 receptor with the Semliki Forest virus system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 225(3):1068–1072
Malhotra AK, Murphy GM Jr, Kennedy JL (2004) Pharmacogenetics of psychotropic drug response. Am J Psychiatry 161:780–796
McMahon FJ, Buervenich S, Charney D, Lipsky R, Rush AJ, Wilson AF, Sorant AJ, Papanicolaou GJ, Laje G, Fava M, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Manji H (2006) Variaton in the gene encoding te serotonin 2A receptor is associated with outcome of antidepressant treatment. Am J Hum Genet 78(5):804–814
Minov C, Baghai TC, Schüle C, Zwanzger P, Schwarz MJ, Zill P, Rupprecht R, Bondy B (2001) Serotonin-2A-receptor and transporter polymorphisms: lack of association in patients with major depression. Neurosci Lett 303(2):119–122
Murphy GM, Kremer C, Rodrigues HE, Schatzberg BA, Schatzberg AF (2003) Pharmocogenetics of antidepressant medication intolerance. Am J Psychiatry 160:1830–1835
Peters EJ, Slager SL, McGrath PJ, Knowles JA, Hamilton SP (2004) Investigation of serotonin-related genes in antidepressant response. Mol Psychiatry 9:879–889
Phillips KA, Veenstra DL, Oren E, Lee JK, Sadee W (2001) Potential role of pharmacogenomics in reducing adverse drug reactions, a systematic review. JAMA 286(18):2270–2279
Reynolds GP, Zhang ZJ, Zhang XB (2002) Association of antipsychotic drug-induced weight gain with a 5-HT2C receptor gene polymorphism. Lancet 359(9323):2086–2087
Reynolds GP, Yao Z, Zhang X, Sun J, Zhang Z (2005) Pharmacogenetics of treatment in first-episode schizophrenia: D3 and 5-HT2C receptor polymorphisms separately associate with positive and negative symptom response. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15(2):143–151
Roden DM, George AL Jr (2002) The genetic basis of variability in drug responses. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1(1):37–44
Sato K, Yoshida K, Takahashi H, Ito K, Kamata M, Higuchi H, Shimizu T, Itoh K, Inoue K, Tezuka T, Suzuki T, Ohkubo T, Sugawara K, Otani K (2002) Association between -1438G/A promoter polymorphism in the 5-HT(2A) receptor gene and fluvoxamine response in Japanese patients with major depressive disorder. Neuropsychobiology 46(3):136–140
Schumacher J, Schulze TG, Wienker TF, Rietschel M, Nothen MM (2000) Pharmacogenetics of the cloazapine response. Lancet 356(9228):506–507
Segman RH, Heresco-Ley U, Finkel B, Inbar R, Neeman T, Schlafman M, Dorevitch A, Yakir A, Lerner A, Goltser T, Shelevoy A, Lerer B (2000) Association between the serotonin 2C receptor gene and tardive dyskinesia in chronic schizophrenia: additive contribution of 5-HT2Cser and DRD3gly alleles to susceptibility. Psychopharmacology 152(4):408–413
Segman RH, Heresco-Levy U, Finkel B., Goltser T, Shalem R, Schlafman M, Dorevitsch A, Yakir A, Greenberg D, Lerner A, Lerer B (2001) Association between the serotonin 2A receptor gene and tardive dyskinesia in chronic schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 6(2):225–229
Serretti A, Kato M, de Ronchi D, Kinoshita T (2007) Meta-analysis of serotonin transporter gene promoter polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) association with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor efficacy in depressed patients. Mol Psychiatry 12:247–257
Sodhi MS, Arranz MJ, Curtis D, Ball DM, Sham P, Roberts GW, Price J, Collier DA, Kerwin RW (1995) Association between clozapine response and allelic variation in the 5-HT2C receptor gene. Neuroreport 7(1):169–172
Tamminga WJ, Wemer J, Oosterhuis B, de Boer A, Vrackx S, Drenth BF et al. (2003) Polymorphic drug metabolism (CYP2D6) and utilisation of psychotropic drugs in hospitalised psychiatric patients: a retrospective study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 59:57–64
Tecott LH, Sun LM, Akana SF et al. (1995) Eating disorder and epilepsy in mice lacking 5-HT2C serotonin receptors. Nature 374:542–546
Wu S, Xing Q, Gao R, Li X, Gu N, Feng G, He L (2005) Response to chlorpromazine treatment may be associated with polymorphisms of the DRD2 gene in Chinese schizophrenic patients. Neurosci Lett 376:1–4
Yuan X, Yamada K, Ishiyama-Shigemoto S, Koyama W, Nonaka K (2000) Identification of polymorphic loci in the promoter region of the serotonin 5HT2C receptor gene and their association with obesity and type II diabetes. Diabetologia 43:373–376
Disclosure
There is no conflict of interest. The authors assure that there is no association with a company whose product is named in the article or a company that markets a competitive product. The presentation of the topic is impartial and the representation of the contents is product neutral.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maier, W., Zobel, A. Contribution of allelic variations to the phenotype of response to antidepressants and antipsychotics. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosc 258 (Suppl 1), 12–20 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-007-1004-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-007-1004-z